Assign Azure SQL Database permissions to Entra users via groups
Scenario
Imagine that you have 100 different Azure SQL Databases in your environment.
What are you gonna do, when you get a new employee that needs access? What if an employee no longer needs permissions? How do you do this most effortlessly?
Do you manually login to each database and run the SQL commands? Nooo, that would take a long time. I propose that you do it via a Entra groups instead, then it literally takes 2 seconds to give permissions to a user.
Microsoft already has it documented that its possible, but they don’t really make it obvious (as of writing this post). It took me some time to figure out that it was possible (maybe i’m not the brightest 😄). So i’m making this post to help you out and show you how i think is good way to do it.
Azure RBAC vs SQL permissions
The first time i had to assign permissions inside an Azure SQL Database to a user, i figured that it could be done via Azure RBAC, that’s how you assign permissions with many of the popular Azure services, but no, that’t not how it works in Azure SQL Database.
Azure RBAC is used to manage the Azure SQL Server and Azure SQL Database resources inside Azure. E.g creating new databases, scaling the Azure SQL Server to get more resources, configuring networking, replicas, etc.
Permissions to read and modify the actual data inside the databases is managed via SQL queries being run on the database server, just like you normally do on-premise.
So in short, permissions inside the database is configured on the database with SQL queries, SSMS etc. Its not done in the Azure portal.
So how are we gonna give database permissions to users, without having to login to the databases and do SQL queries?
I propose that you create groups in Entra. Then login to the databases and give “database-level roles” to those groups.
Now all you have to do to give access to a new user, is to add them to the Entra group.
SQL query
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
-- If you are having issues, then remember to specifiy database when connecting;
-- Remember to use an Entra user to run this query, since you cannot add entra uses with a normal SQL account;
-- Statement to see which database you are connnected to;
-- If you don't specifiy database when connecting, then you are probably connected to the master database.
-- SELECT db_name() as DatabaseYouAreConnectedTo;
-- Create Microsoft Entra Group for Azure SQL Database;
CREATE USER [groupName] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
-- Add the group to a role;
EXEC sp_addrolemember 'paste-database-level-role-here','groupName';
Example
Prerequisite
When you create an Azure SQL Server, then you can choose between these 3 authentication methods. I’m gonna assume you already choose either “Only Microsoft Entra-only authentication” or “Both SQL and Microsoft Entra authentication”.
- Only Microsoft Entra-only authentication.
- Both SQL and Microsoft Entra authentication.
- Only SQL authentication.
I’m also gonna assume you can create the Entra groups yourself.
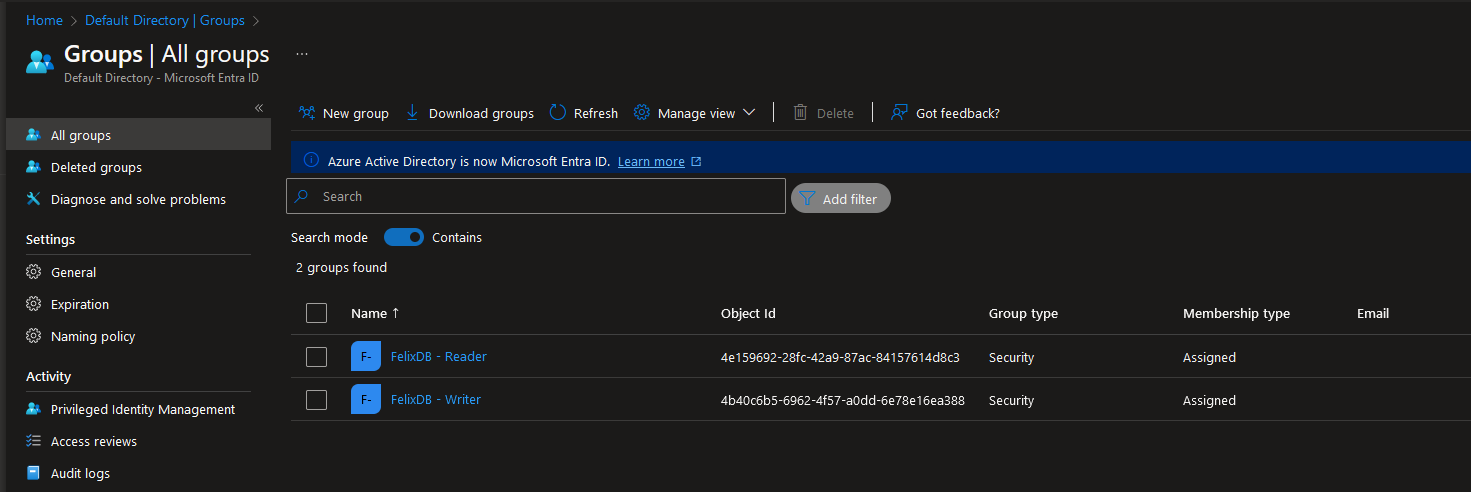
1) Permissions i want to delegate.
| Group | Permissions | Members |
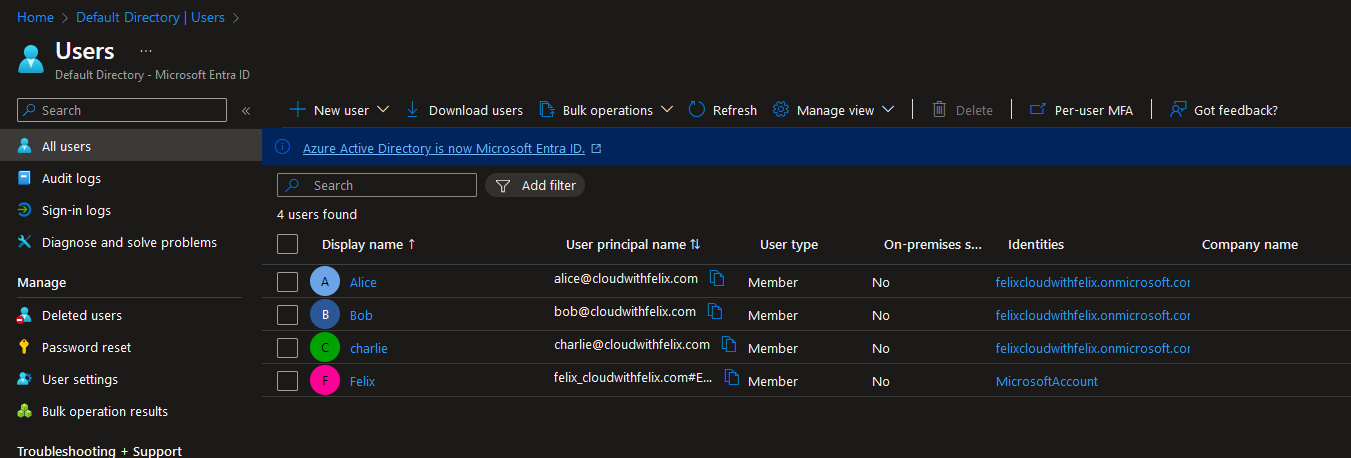
| FelixDB – Reader | Read | Bob |
| FelixDB – Writer | Read/write | Alice |
2) Logging in
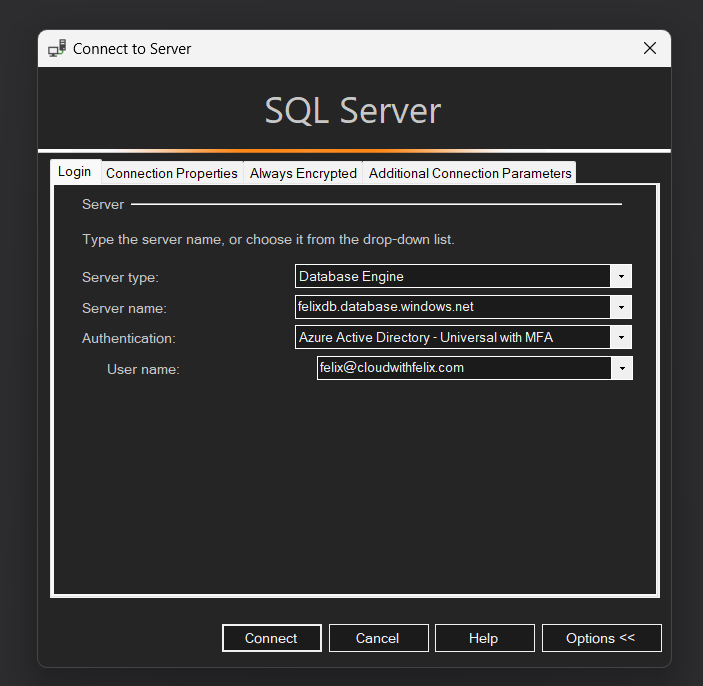
I’m gonna start by connecting to the database using an Entra account, you cannot use an SQL account for this! You need to use an Entra user.
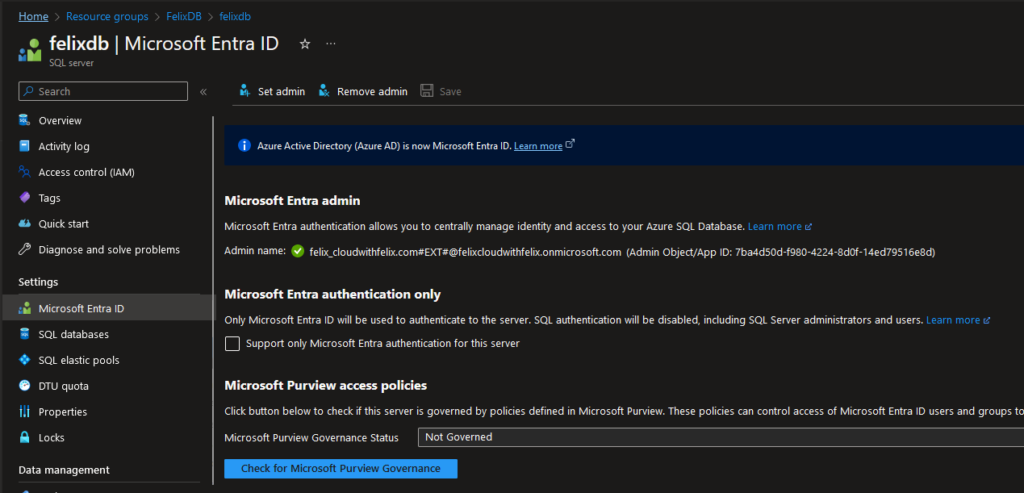
If you don’t know who has access to the server, then use the “Microsoft Entra admin” account. This user will always have the db_owner role.
Remember to specify the correct database when connecting (because contained users). I’m using SQL Server Management Studio to connect.
3) Delegating permissions to groups
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
-- If you are having issues, then remember to specifiy database when connecting.
-- Remember to use an Entra user to run this query, since you cannot add entra uses with a normal SQL account.
-- Statement to see which database you are connnected to.
-- If you don't specifiy database when connecting, then you are probably connected to the master database.
SELECT db_name() as DatabaseYouAreConnectedTo;
-- Create Microsoft Entra Group for Azure SQL Database.
CREATE USER [FelixDB - Reader] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
-- Add the group to a role;
EXEC sp_addrolemember 'db_datareader','FelixDB - Reader';
-- Create Microsoft Entra Group for Azure SQL Database.
CREATE USER [FelixDB - Writer] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
-- Add the group to a role;
EXEC sp_addrolemember 'db_datareader','FelixDB - Writer';
EXEC sp_addrolemember 'db_datawriter','FelixDB - Writer';
4) Checking your work
You can use the following SQL query to see if your Entra groups has the correct roles.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
SELECT DP1.name AS DatabaseRoleName,
isnull (DP2.name, 'No members') AS DatabaseUserName
FROM sys.database_role_members AS DRM
RIGHT OUTER JOIN sys.database_principals AS DP1
ON DRM.role_principal_id = DP1.principal_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.database_principals AS DP2
ON DRM.member_principal_id = DP2.principal_id
WHERE DP1.type = 'R'
ORDER BY DP1.name;
Since this is a test environment and i have logins for both Both and Alice, then i’m also gonna login as them, and see if they are able to read, and in the case of Alice also write.
Sources
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/logins-create-manage?view=azuresql
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/security-server-roles?view=azuresql
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/authentication-aad-overview?view=azuresql